Maureen Data Systems
Platform as a Service
Lower Costs
Affordable access to a wider variety of resources. PaaS platforms typically offer access to a wider range of choices up and down the application stack— including operating systems, middleware, databases and development tools.
Faster Deployment
Faster time to market. With PaaS, there’s no need to purchase and install the hardware and software you use to build and maintain your application development platform—and no need for development teams to wait while you do this.
Flexible & Scalable
More freedom to experiment, with less risk. PaaS also lets you try or test new operating systems, languages and other tools without having to make substantial investments in them, or in the infrastructure required to run them.
Platform as a service
Platform-as-a-Service, is a cloud computing model that provides customers a complete cloud platform—hardware, software, and infrastructure—for developing, running, and managing applications without the cost, complexity, and inflexibility that often comes with building and maintaining that platform on-premises.
The PaaS provider hosts everything—servers, networks, storage, operating system software, databases, development tools—at their data center. Typically customers can pay a fixed fee to provide a specified amount of resources for a specified number of users, or they can choose ‘pay-as-you-go’ pricing to pay only for the resources they use. Either option enables PaaS customers to build, test, deploy run, update and scale applications more quickly and inexpensively they could if they had to build out and manage their own on-premises platform.
Every leading cloud service provider—including Amazon Web Services (AWS), Google Cloud, IBM Cloud and Microsoft Azure—has its own PaaS offering. Popular PaaS solutions are also available as open source projects (e.g. Apache Stratos, Cloud Foundry) or from software vendors (e.g. Red Hat OpenShift and Salesforce Heroku).
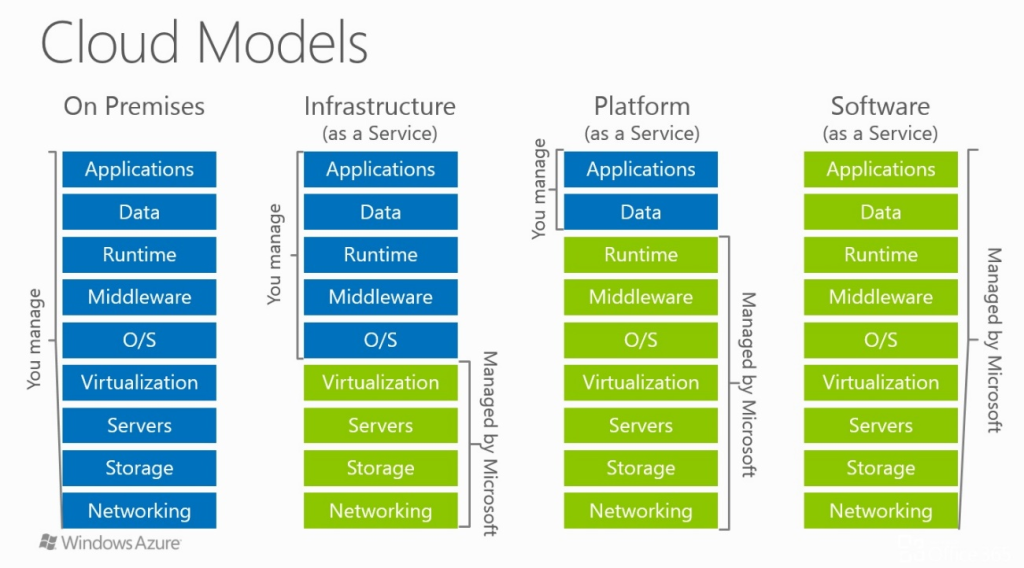

Benefits of PaaS
Lift-and-shift migration
This is the fastest and least expensive method of migrating an application or workload to the cloud. Without refactoring your underlying architecture, you can increase the scale and performance, enhance the security, and reduce the costs of running an application or workload.
Test and development
Your team can quickly set up and dismantle test and development environments, bringing new applications to market faster. IaaS makes it quick and economical to scale dev/test environments up and down.
Storage, backup, and recovery
Your organization avoids the capital outlay for storage and the complexity of storage management, which typically requires a skilled staff to manage data and meet legal and compliance requirements. IaaS is useful for handling unpredictable demand and steadily growing storage needs. It also can simplify planning and management of backup and recovery systems.
Web apps
IaaS provides all the infrastructure to support web apps, including storage, web and application servers, and networking resources. Your organization can quickly deploy web apps on IaaS and easily scale infrastructure up and down when demand for the apps is unpredictable.
High-performance computing
High-performance computing on supercomputers, computer grids, or computer clusters helps solve complex problems involving millions of variables or calculations. Examples include protein folding and earthquake simulations, climate and weather predictions, financial modeling, and product design evaluations.
Use Cases of PaaS
By providing an integrated and ready-to-use platform—and by enabling organizations to offload infrastructure management to the cloud provider and focus on building, deploying and managing applications—PaaS can ease or advance a number of IT initiatives, including:
- API development and management: Because of its built-in frameworks, PaaS makes it much simpler for teams to develop, run, manage and secure APIs (application programming interfaces) for sharing data and functionality between applications.
- Internet of Things (IoT): Out of the box, PaaS can support a range of programming languages (Java, Python, Swift, etc.), tools and application environments used for IoT application development and real-time processing of data generated by IoT devices.
- Agile development and DevOps: PaaS can provide fully-configured environments for automating the software application lifecycle including integration, delivery, security, testing and deployment.
- Cloud migration and cloud-native development: With its ready-to-use tools and integration capabilities, PaaS can simplify migration of existing applications to the cloud—particularly via replatforming (moving an application to the cloud with modifications that take better advantage of cloud scalability, load balancing and other capabilities) or refactoring (re-architecting some or all of an application using microservices, containers and other cloud-native technologies).
- Hybrid cloud strategy: Hybrid cloud integrates public cloud services, private cloud services and on-premises infrastructure and provides orchestration, management and application portability across all three. The result is a unified and flexible distributed computing environment, where an organization can run and scale its traditional (legacy) or cloud-native workloads on the most appropriate computing model. The right PaaS solution allows developers to build once, then deploy and mange anywhere in a hybrid cloud environment.







Client Testimonials
Maureen Data Systems
Why Choose Us?

Strategy
We meet you where you are in your technical journey to develop a roadmap for success.

Execution
We deliver end-to-end IT and digital transformation solutions across different ecosystems.

Continuity
We ensure operational readiness and transition you from projects to managed services seamlessly.
